Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems streamline business operations by centralizing essential functions like personnel, finance, and inventory management. Businesses may stay organized, cut down on errors, and save time by using Enterprise Resource Planning Types or ERP type. ERP systems are critical to the efficient operation of enterprises. Imagine if your favorite business consistently carried the correct items or if employees were paid on schedule and without any issues. All ERP systems assist with that!
There are different types of ERP systems available, designed to suit different kinds of enterprises. Some are better ERP Suite for small businesses, while others are designed for large ones. With ERP deployment challenges, you may even select how you want your ERP to function. Businesses can choose between having the software on their desktops, on the cloud, or a combination of both using these models. Businesses benefit greatly from ERP systems since they save money and foster expansion. They facilitate future planning and visibility into the company's operations. It's wise to weigh your alternatives and select the ERP system that best suits your demands because selecting the correct one is crucial.
We'll discuss types of ERP systems, their functions, and how they can support the growth of companies much like yours in this blog. To find out more about these incredible technologies, stay tuned! There are types of enterprise resource planning solutions available, designed to suit different kinds of enterprises. Understanding what types of ERP systems are there can help businesses choose the right solution.
What is ERP Systems?
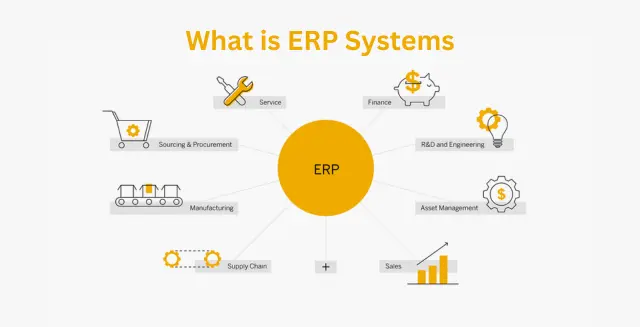
Understanding ERP types of systems allows businesses to select the most efficient software for their needs, whether on-premise, cloud-based, or hybrid solutions. An ERP system's primary objective is to simplify and speed up work, and it’s important to explore what are the different types of ERP solutions to select the best fit. ERP systems are tools that make it easier and more organized for organizations to manage their everyday tasks.
Companies often ask what is ERP and its types, as there are different ERP solutions designed for various industries. ERP systems are tools that make it easier and more organized for organizations to manage their everyday tasks, and there are types of ERPs available for different industries and business needs. They are a kind of business management software that unifies several tasks in a single location. These responsibilities may include supply chain management, inventory tracking, financial management, and staff care.
An ERP system's primary objective is to simplify and speed up work. It accomplishes this by consolidating all significant corporate operations into a single, centralized platform. This implies that a company can use a single system rather than a variety of tools. ERP systems are essential Digital Transformation Tools, enabling businesses to integrate operations and achieve excellence.
The fact that ERP systems gather data from every aspect of the company is one of its strongest features. They keep this data in a single database that is accessible to all employees. This prevents misunderstandings and improves teamwork. Because they can view all the data in one location, managers are also able to make decisions more quickly.
Businesses can cut down on errors and save time by implementing an ERP system with advanced ERP systems functionality that automates various processes. For instance, it helps keep track of stock levels so that customers don't have to wait. To ensure accuracy, it also maintains records of payments and sales.
Additionally, using an ERP system facilitates collaboration within the company. Workers are able to better plan their work by seeing what is going on in other departments. This enhances collaboration and streamlines business operations.
ERP systems function similarly to a very intelligent business assistant, offering different ERP software types based on company size and needs. They simplify, expedite, and organize the management of everything.
What Does ERP Systems Do?
.webp)
ERP systems carry out a number of vital tasks for a company, and choosing the right type of ERP systems ensures smooth business operations, and different ERP system types cater to these specific business needs. To learn what does ERP systems do, let's examine some of the fundamental roles:
Effective Demand Forecasting and Lean Inventory
ERP systems are excellent resources for companies looking to improve their planning and steer clear of stock-related issues. Demand forecasting, which assists companies in estimating the quantity of a product they will require, is one of their best benefits. This ensures they maintain adequate stock without over- or under-ordering.
ERP software development system displays real-time information on what customers are purchasing and the amount of stock that is available. To assist firms in determining when to increase or decrease their orders, these tools examine patterns and trends. Lean inventory, or maintaining precisely the correct quantity of goods, is the result of this astute planning.
Lean Inventory is particularly beneficial because it saves money and minimizes waste. Companies may prevent running out of popular things and don't have to keep extra items they won't sell. Because companies know precisely when to place new stock orders, it also facilitates the seamless operation of supply networks.
Businesses may make better inventory decisions with ERP systems. They can maintain client satisfaction, prevent losses, and perform more effectively. It's a straightforward and astute method of maintaining order.
Reduce Production Bottlenecks
ERP solutions are incredibly beneficial to manufacturing companies. They function similarly to an intelligent tool that identifies issues, or bottlenecks, in the manufacturing process. Manufacturing ERP software allows managers to swiftly identify and address areas of delay.
One of these systems' primary features is real-time tracking, which is available in different types of ERP software for better data management. which is available in various ERP systems to optimize manufacturing processes. It displays the current state of affairs on the production line. This aids companies in improving their production planning and decision-making. They can prevent time and resource waste by better arranging their work.
Workflows are also made more efficient by ERP systems. There are fewer delays when everyone is aware of what has to be done and when. This enables companies to satisfy customers and accomplish production goals on schedule.
Manufacturers can work more quickly and save money by utilizing ERP systems. Without overtaxing their systems, they are able to generate the appropriate quantity of items. It functions similarly to a clever assistant that maintains things in order.
One excellent strategy to lessen production bottlenecks is to implement ERP systems. They support the efficient operation, timely product delivery, and successful expansion of manufacturing companies. ERP systems, functioning as Integrated Business Systems, streamline processes to reduce production bottlenecks effectively
Transparency Through the Business
An ERP or other integrated business solution clarifies how a business operates. Everyone can view the same, most recent information because all the data is kept in one location. Teams can collaborate more easily and come to wiser judgments as a result. For instance, staff members have the ability to view sales data, inventory levels, and financial information at any time.
Everyone in the organization stays in sync while using real-time data. You don't have to guess what's going on or wait for updates. Workers can make better plans, and managers can monitor progress. Because all the information is readily available, it also speeds up issue solving.
Businesses can function more efficiently by implementing an ERP system. People work smarter, not harder, thanks to it. Enterprise Resource Planning examples illustrate how businesses can use ERP systems to achieve transparency across departments by centralizing information and automating workflows.
Benefits of ERP Systems
.webp)
A company can gain a lot by implementing an ERP system. Here are a few of the main benefits:
Cost Savings
Businesses can save money in a variety of ways with an ERP system. Data input and order tracking are two examples of the manual chores that it automates. As a result, there will be fewer errors and lost time. Businesses can save money and prevent expensive issues by decreasing errors.
Cost savings is one of an ERP's main advantages. Companies can save unnecessary costs, such as manual labor or paper. Instead than doing the same work over and over, teams can concentrate on more vital duties. This improves the efficiency of the entire business.
ERP ROI (Return on Investment), or return on investment, is another crucial component. The long-term benefits that an ERP system generates outweigh the Initial investment costs. Businesses may accomplish more with fewer resources and save overhead expenses.
ERP systems are clever instruments for productivity and cost reduction. They enable companies to accomplish more with less work.
Increased Productivity
ERP systems improve business operations. They streamline and systematize the process of completing activities. This eliminates the need for workers to waste time on monotonous tasks like repeatedly entering the same data. They might instead concentrate on crucial aspects that support the expansion of the business.
Tasks are made easier and faster with operational efficiency. ERP systems facilitate rapid information sharing by connecting all departments. Teams are able to collaborate more quickly thanks to this. It is possible to solve issues more quickly and make more intelligent decisions.
Business process improvement is an additional advantage. ERP systems assist businesses in identifying more efficient methods of operation. They assist in resolving those problems by highlighting areas where time or resources are being wasted. This increases productivity and streamlines operations.
Businesses may accomplish more in less time when they employ an ERP. Employees work smarter, not harder, thanks to it. This eventually results in significant gains in the business's performance. By enabling the Automation of Tasks, ERP systems boost productivity and allow employees to focus on strategic activities.
Regulatory Compliance ERP
Businesses must abide by stringent regulations in several areas. By automating crucial processes, ERP systems assist companies in adhering to these regulations. They ensure that everything is completed in compliance with the necessary requirements. They can, for instance, keep tabs on procedures, generate reports, and verify that all activities adhere to rules.
ERP solutions make compliance management simpler. These systems ensure that all data is accurate and well-organized, preventing confusion. They also notify companies when something is not in compliance with the regulations. By doing this, errors that can result in penalties or other issues are avoided.
A Regulatory Adherence ERP guarantees that businesses are always prepared for inspections or audits. It produces unambiguous documentation of procedures, which is crucial for fulfilling industrial standards. In addition to saving time, this increases regulator and customer trust.
Businesses may concentrate on their job without worrying about breaking any rules when they have an ERP system in place. It simplifies and eases compliance.
How to Optimize Your ERP System for Scalable Success
.webp)
It's critical to ensure that your ERP system continues to function efficiently as your company expands. Choosing the right ERP system is crucial to ensure your business can scale effectively. Choosing the right ERP system is crucial for business success, and companies should evaluate ERP system options to match their operational goals. Business owners often ask what are different ERP systems, as there are multiple solutions tailored for different industries. If you're unsure about how to approach this decision, the How to Select the Right ERP System guide provides detailed steps and considerations to make an informed choice that aligns with your organization's needs. These easy pointers will assist you in optimizing your ERP system.
Customization
Since every company is different, your ERP system should be tailored to meet your needs. Numerous ERP systems allow for customization. This implies that you can align the system with your workflows, which will facilitate everyone's work. You may maximize the benefits of your ERP by customizing it.
Cloud-Based Solutions
Selecting an ERP system that runs on the cloud services is a wise choice. Scalable ERP Solutions enable you to expand or contract your system in response to changes in your company. You don't need to worry about purchasing additional servers or hardware when using a cloud ERP solution. It is adaptable and easy to change to meet your demands. For businesses considering cloud options, understanding the advantages of Cloud ERP can be a crucial factor in decision-making. These solutions streamline business operations and provide real-time updates, which are essential for modern enterprises.
Training and Support
Your team must be able to use the ERP system for it to be useful. Ensure that everyone receives the appropriate training. Better outcomes can be achieved when a team that has received proper ERP training programs makes the most of the ERP. Additionally, make sure your ERP vendor provides quality support when you need it.
Regular Updates
Your ERP system should be able to adapt to the rapid advancements in technology. Your system will remain up to date with new features and enhancements if you do regular updates. Updates also enhance performance and address issues. Verify whether your provider provides frequent system updates and assistance.
You may prepare your ERP system for the future by concentrating on these actions. An ERP that is properly optimized facilitates trouble-free corporate growth. It's similar to laying a solid basis for sustained success. It’s also useful to consider what are some ERP systems that competitors or similar businesses use to gain insights into industry best practices.
Types of ERP Software: Exploring Different ERP Systems for Businesses
.webp)
ERP systems allow businesses to manage processes more efficiently, and understanding what are the different ERP systems can help companies select the right one. There are many types of ERP systems, each tailored to the requirements of distinct business sizes and industries. Understanding the Cloud vs On-Premise ERP debate can help companies select the right model based on their infrastructure, budget, and business needs. Companies often ask how many types of ERP software exist; the answer depends on industry needs, deployment models, and customization options. Some of the most well-liked ERP options on the market right now are listed below:
Oracle NetSuite
Oracle NetSuite is a robust ERP program that supports company expansion. Because of its well-known scalability of ERP, it can readily adapt to companies of any size. NetSuite offers capabilities to suit your needs, regardless of the size of your business. It facilitates Sales Order Processing, customer relationship management (CRM), and financial management.
The fact that Oracle NetSuite is a cloud-based ERP solution is among its strongest features, making it one of the most common ERP systems used by businesses today. This implies that companies can use it at any time and from any location. It doesn't require bulky hardware and is simple to set up. Because of this, it's a fantastic option for businesses seeking a straightforward, adaptable solution to run their operations.
Additionally, NetSuite has numerous tool connectors, which increases its value for companies. One of the reasons it is so well-liked, particularly by cloud-based businesses, is its capacity to interface with various platforms and services. All things considered, Oracle NetSuite is a dependable and effective ERP solution that aids companies in effectively managing their operations and expanding without boundaries.
Intuit QuickBooks
Additionally, NetSuite has numerous tool connectors, which increases its value for companies. One of the reasons it is so well-liked, particularly by cloud-based businesses, is its capacity to interface with various platforms and services. All things considered, Oracle NetSuite is a dependable and effective ERP solution that aids companies in effectively managing their operations and expanding without boundaries.
The inventory management feature of QuickBooks is an additional advantage. It enables companies to monitor their inventory levels and items. This can save money by preventing overordering or running out of inventory.
All things considered, small businesses that want a dependable ERP system to handle their accounts, orders, and inventory should consider Intuit QuickBooks. It is inexpensive, user-friendly, and covers a wide range of crucial duties to maintain a successful business.
Sage Intacct
Sage Intacct is well known for its robust financial management features in cloud-based ERP systems. It is ideal for companies that need to manage their money wisely. Businesses can simply generate accurate financial reports with the help of Sage Intacct. Businesses can better comprehend their financial health with the use of these reports.
The budgeting tools of Sage Intacct are among its primary features. Businesses may remain on top of their expenditure by using it to plan and monitor their budget. This facilitates improved decision-making and helps prevent expenditures.
Additionally, Sage Intacct has tools for supply chain and inventory management. This aids companies in monitoring their goods and making sure everything functions properly. Sage Intacct gives the capabilities to make it simple whether you need to track orders or manage stock.
All things considered, companies in need of a dependable, cloud-based ERP solution should consider Sage Intacct. It integrates supply chain and inventory management modules with robust financial management and financial reporting solutions. It is a comprehensive solution that aids in the growth and organization of enterprises.
SAP Business One
An ERP system designed for small and medium-sized enterprises is SAP Business One. It facilitates the management of crucial company domains, including production, sales, inventories, and finances. It is simpler to keep track of everything in one location using this system.
SAP Business One's robust analytics are among its best qualities. It can produce reports that give companies insight into their performance. This aids businesses in making more informed decisions based on actual data.
Additionally, SAP Business One integrates seamlessly with other SAP products, such as SAP S/4HANA, facilitating the addition of additional capabilities as needed by enterprises. Because of its adaptable ERP infrastructure, this system may expand together with your company. You may easily add additional features to SAP Business One as your business grows.
The system is renowned for being simple to integrate and set up. It streamlines operations to help organizations become more efficient. Businesses may improve process management and obtain insightful data for expansion with SAP Business One. For companies searching for strong tools without complexity, it is a comprehensive ERP system.
Xero
For small enterprises, Xero is an excellent cloud-based ERP system. It has basic accounting capabilities and is user-friendly. You can easily keep track of your earnings and outlays with Xero. Additionally, it assists you in cash flow management by ensuring that you are aware of the precise location of your funds.
Xero offers inventory management solutions in addition to accounting. This aids companies in monitoring orders and stock levels. Additionally useful is the invoicing feature, which enables companies to promptly issue and monitor bills.
Another well-known feature of Xero is its robust reporting capabilities. It produces readable reports that assist companies in comprehending their financial status. Sharing these reports with your accountant or team will facilitate planning and decision-making.
Because Xero is a cloud-based ERP, you can access your data at any time and from any location. You don't have to be concerned about costly software or difficult installations. It's a cost-effective option for companies looking for a dependable, user-friendly system to handle inventory, finances, and other tasks.
Zoho Finance
A component of the Zoho suite, Zoho Finance provides a range of tools to assist companies in managing their money. It makes keeping track of your finances simple with its capabilities for billing, invoicing, and financial reporting.
Zoho Finance's expense management features are among its main advantages. Tracking and classifying your spending makes it simple to see where your money is going. This aids companies in managing their money and making wiser choices.
Additionally, Zoho Finance has useful automation tools. These technologies provide the ability to track payments, send reminders, and create invoices automatically. This minimizes errors and saves time. Companies can concentrate on other crucial areas since they are not required to perform every task by hand.
For small firms seeking an easy-to-use and reasonably priced system, this all-in-one ERP solution is fantastic. For businesses who need to handle funds and expenses and use automation to expedite their job, Zoho Finance is an affordable option. Zoho Finance's extensive feature set makes money management easy and effective.
FreshBooks
FreshBooks is an extremely user-friendly cloud-based ERP system. For small firms and independent contractors that need to handle their finances, it is particularly beneficial. Automated invoicing systems, which make billing clients quick and easy, are one of its key benefits. To save time and cut down on errors, you can configure invoices to send automatically.
Financial planning and analysis (FP&A) software is another area in which FreshBooks excels. It helps companies make better financial decisions by enabling them to monitor their revenue and expenses. You can use this tool to generate reports that clearly illustrate your financial situation.
FreshBooks provides time tracking and project management capabilities in addition to financial and invoicing solutions. Businesses who need to monitor the progress of many initiatives will find this useful. You may keep track of the amount of time spent on each task and adjust your customer bills accordingly.
All things considered, FreshBooks is a fantastic option for freelancers or small enterprises searching for an easy-to-use and reasonably priced ERP system. It combines simple time tracking and project management software with robust accounting and invoicing facilities in one location.
Microsoft Dynamics 365
One robust ERP option that is suitable for medium-sized to large enterprises is Microsoft Dynamics 365. It gives firms options for managing operations, sales, and finances in a single system by combining CRM and ERP functions.
The seamless integration of Microsoft Dynamics 365 with other Microsoft products, such as Word, Excel, and Outlook, is one of its main advantages. This makes it simple and hassle-free for companies that already use Microsoft tools to add and connect Dynamics 365. Businesses may maintain all of their data in one location with the help of this ERP integration.
Businesses can monitor their finances and make smarter decisions with the help of Dynamics 365's robust financial management features. It is a comprehensive solution for expanding enterprises, with capabilities to manage sales and enhance client connections.
Businesses looking to optimize their operations and integrate with other Microsoft tools will find this ERP system particularly useful. Businesses may more easily handle all of their everyday responsibilities, from financial administration to sales, with Microsoft Dynamics 365.
SAP ERP
Large companies employ SAP ERP, a robust and comprehensive system. It has modules for a wide range of corporate domains, including supply chain management, manufacturing, human resources, and finance. For large organizations that must oversee numerous operations concurrently, this makes it an excellent option.
Businesses use SAP ERP mostly because of its scalability and resilience. It can manage massive volumes of data and develop alongside your company as it grows. Whether your business is tiny currently or expanding rapidly, SAP ERP may be tailored to your requirements.
SAP makes it simple to set up and integrate ERP implementation into your company. It assists companies in connecting various departments and organizing their data.
Data-drivenness is another characteristic of SAP ERP. It enables companies to gather and examine data from every aspect of their business operations. This aids businesses in making informed decisions based on up-to-date data.
All things considered, SAP ERP is a fantastic option for big businesses that require a system to oversee every aspect of their operations. It is an effective instrument for success, helping with everything from supply chain management to finances.
Deltek
Deltek is an ERP system designed for project-oriented organizations. Businesses in the engineering, construction, and professional services sectors particularly benefit from it. Deltek offers tools to assist in managing every aspect of a project, from inception to completion.
Deltek's Project Management ERP capabilities are among its primary features. These technologies make it simple for organizations to plan, monitor, and oversee projects. Tasks, due dates, and budgets may all be tracked in one location. This guarantees that projects are finished on schedule and keeps teams organized.
Deltek's Project Accounting ERP functionalities are also robust. It assists companies with project-related expense tracking, invoice management, and payment processing. For businesses who need to closely monitor their expenditure and make sure they stay within their budget, this is quite beneficial.
Deltek's popularity stems from the fact that it was designed for companies who frequently undertake projects. It helps them remain on course and prevent errors by providing them with the resources they need to oversee both the project and its financial components. An excellent ERP option for your company is Deltek if it works on projects.
Multiview ERP
Small and mid-sized enterprises can benefit from Multiview ERP, a financial management solution. It is intended to simplify money management. Accounting, budgeting, and financial reporting modules are available in Multiview ERP. This aids companies in maintaining organization and financial management.
Multiview ERP's Financial Consolidation ERP is one of its primary functions. This enables companies to compile financial information from various divisions or sites into a single, understandable report. It facilitates comprehension of the company's overall financial situation.
Business intelligence tools are also available in Multiview ERP. These tools assist managers in making informed decisions by analyzing the financial data of the company. Businesses may track performance, identify trends, and enhance their strategies with the help of business intelligence.
The system is renowned for being quick to set up and simple to operate. It doesn't take a lot of technical assistance expertise to launch a small or midsized business. Through the provision of transparent reporting and accounting and budgeting tools, Multiview ERP assists companies in enhancing their financial management. It is an excellent option for businesses seeking a straightforward yet effective financial management system.
Acumatica Cloud ERP
The ERP system Acumatica Cloud ERP was created with expanding companies in mind. It is adaptable and can grow with your company as it does. Acumatica is a comprehensive solution for a wide range of requirements because it provides ERP modules for financials, project management, CRM, and more.
The Multi-Tenant Cloud ERP feature of Acumatica is one of its primary advantages. This implies that companies only need an internet connection to access the system from any location. Since the system is cloud-based, server and installation management is not a concern.
Acumatica Cloud ERP is renowned for its user-friendliness. Even if employees lack technological expertise, the system is made to be easy for them to grasp. Additionally, it has capabilities that can be customized, enabling companies to modify the system to meet their own requirements.
Acumatica Cloud ERP offers the appropriate capabilities for project monitoring, money management, and customer relationship enhancement. Businesses who are growing or require a system that can adapt to their needs will find it to be a great option due to its scalability and flexibility. Acumatica increases productivity and simplifies corporate management.
Oracle ERP Cloud
A cloud-based software program called Oracle ERP Cloud was created to assist big enterprises in running their operations. Project management, procurement, and finance management are just a few of its numerous functions.
This makes it an excellent tool for companies that need to manage projects, purchase items, or keep track of finances. Because Oracle ERP Cloud can grow with the business, it is particularly beneficial for rapidly expanding organizations.
ERP Migration services can facilitate the seamless transfer of data and procedures when a company wishes to shift from another system to Oracle ERP Cloud. Professionals provide a smooth and rapid transfer. ERP Consulting Services can also assist businesses with system setup and personnel training.
It is simpler to comprehend how Oracle ERP Cloud can enhance day-to-day operations thanks to these features.
The system is adaptable and may be tailored to meet various company requirements. Businesses can increase productivity, save time, and make better decisions using Oracle ERP Cloud. For businesses seeking a dependable and potent ERP system to expand and maintain their competitiveness in their sector, it's a fantastic option.
Syspro
A manufacturing ERP system called Syspro was created to assist businesses in managing their procurement, inventory, and production procedures. Manufacturers and distributors who need to monitor raw materials, production schedules, and final products may find it very helpful. Syspro helps companies make sure they have what they need when they need it and streamline operations.
Businesses may enhance their supply chain management by monitoring and streamlining the flow of goods from suppliers to consumers with Syspro. Order management is made simpler, waste is decreased, and manufacturing efficiency is guaranteed using this system.
Businesses looking for a manufacturing-focused ERP system frequently choose Syspro. It assists companies in cutting expenses, enhancing the caliber of their output, and maintaining operational control. The entire manufacturing process may be managed services more efficiently and effectively with the help of this ERP system.
TallyPrime
An ERP program called TallyPrime was created with small and medium-sized enterprises in mind. It tracks stock levels, orders, and delivery and assists firms with inventory management. This facilitates organization and guarantees that goods are available when needed.
Accounting and payroll processing are among the other functions that TallyPrime offers. It enables companies to create reports, handle staff wages, and manage their finances. TallyPrime also functions as an ERP system for financial forecasting, assisting companies in making plans for upcoming costs and income. Making wise financial decisions is facilitated by this.
Because of its reputation for being easy to use, TallyPrime is perfect for small firms that require an ERP system that is both straightforward and effective. From inventory control to financial forecasting, it assists business owners in maintaining the smooth and effective operation of their enterprises.
Epicor
Epicor is a global ERP solution that aids companies in financial, supply chain, and manufacturing management. It is renowned for being adaptable, which makes it appropriate for a variety of businesses.
Epicor's ERP System for Project Management, which aids companies in effectively planning, monitoring, and managing their projects, is one of its primary features. It enables teams to control expenses while maintaining organization and meeting deadlines.
To assist companies in managing their manufacturing operations, Epicor also provides production planning tools. This function guarantees timely product creation, seamless production, and the availability of supplies when needed.
For companies seeking an ERP solution that can be customized, Epicor is the best option. Because of its industry adaptability, it is a useful tool for businesses looking to increase productivity and streamline processes.
Odoo
Odoo is an ERP system that is open-source and has several features. It has modules for HR, inventory control, accounting, and other areas. For companies of all sizes, this makes it a versatile solution.
Odoo's ERP Customization capabilities is one of its key benefits. Companies can modify the system to meet their IT team requirements. Odoo may be customized to meet the needs of each business, whether that means changing or adding new features.
Business Process Automation is another essential component. Order management and inventory tracking are just two of the numerous operations that Odoo helps organizations automate. This increases efficiency, decreases human error, and saves time. Odoo's user-friendly interface makes it easier for businesses to increase productivity and streamline processes.
For companies seeking an ERP solution that is adaptable and can expand with them, Odoo is ideal.
Extensiv
For companies in the supply chain and logistics sectors, Extensiv is a cloud-based ERP deployment. It provides a number of tools to assist in managing various facets of corporate operations.
Logistics Optimization is one of Extensiv's primary functions. This aids companies in cutting expenses and increasing the effectiveness of their supply chain. It helps guarantee on-time product delivery and streamlines procedures.
Additionally, the system has strong Order Management capabilities. Order management, including inventory tracking and processing, is simple for businesses. Businesses can accurately track orders and inventories thanks to Extensiv's real-time updates.
Businesses trying to boost overall efficiency and logistical operations will find this ERP solution particularly helpful. Businesses may stay organized and efficiently satisfy consumer requests with the use of Extensiv's products.
What Are ERP Features?
.webp)
Numerous capabilities provided by ERP systems assist companies in streamlining their processes. Modern ERP systems benefit from Continuous Integration and Continuous Delivery, ensuring smoother updates and faster deployment of new features. ERP systems help businesses streamline processes, and evaluating types of ERP softwares ensures that businesses select solutions that align with their size and industry, and the ERP system functions define how well it integrates with different business units. The following are a some of the most typical ERP features:
Financial Management
ERP systems offer robust financial management capabilities that support efficient financial management for enterprises, with different type of ERP software designed to meet unique business needs. These tools have financial reporting, accounting functionality, budgeting and forecasting. These features make it simple for firms to keep track of their revenue recognition and expenses. It enables individuals to make wise judgments and comprehend where their money is going.
An ERP system's financial management features also guarantee that companies stay error-free and in compliance with rules. Businesses may plan their budget, generate accurate financial reports, and obtain a comprehensive understanding of their financial health by utilizing these tools. Businesses find it simpler to remain organized and make wise decisions as a result.
Accounting
ERP systems include comprehensive accounting modules that facilitate easy financial management for enterprises. These modules have functions for payroll, tax computations, and accounts payable and receivable. Businesses can use these tools to keep track of the money they owe other people and the money that other people owe them.
This guarantees timely payment collection and timely bill payment. Companies can more easily remain on top of their financial obligations thanks to the system's assistance in managing staff wages and tax calculations. Businesses can prevent errors and maintain accurate records by having all of this information in one location. This helps organizations save time and cut down on errors by simplifying and improving financial administration.
Order Processing
One crucial component of ERP systems is order processing. From the time a consumer placed an order until it is shipped, it assists businesses in tracking those orders. By ensuring that orders are processed promptly, the system minimizes errors and delays. Companies can easily monitor the status of every order, which simplifies shipment management.
Businesses may prevent mistakes like mailing the incorrect items or missing deadlines by using order processing software. This guarantees accurate deliveries and satisfied consumers. Businesses can increase productivity and maintain organization by handling orders through ERP systems. This facilitates business operations and saves time.
Project Management
Project management solutions are included with ERP systems to assist companies in project planning and monitoring. Setting objectives, allocating responsibilities, and tracking results are made simple by these tools. They also aid in the management of people, money, and time. With the system's collaboration features, teams may collaborate more effectively.
ERP project management guarantees that deadlines are fulfilled and nothing is overlooked. With updates and shared information, it also keeps everyone informed. Businesses can successfully complete projects and prevent confusion by utilizing these tools. Teams stay organized and work runs more smoothly as a result.
Embedded AI
AI is integrated systems into some ERP systems to speed up and improve corporate operations. Businesses may better comprehend their data with the help of this feature, which offers real-time insights.
Businesses may anticipate trends, uncover untapped opportunities, and swiftly resolve issues using embedded AI. It can save time and effort by recommending the optimal course of action. By automating repetitive processes, AI tools also help to eliminate human mistake. For instance, they are better able to predict demand or examine sales trends.
This enables companies to remain ahead of the competition and make better judgments. Businesses may increase productivity and concentrate on expansion by implementing embedded AI. ERP systems are now even more lucrative and powerful thanks to this cutting-edge technology.
Real-Time Data
ERP systems offer real-time data, which makes them powerful. As a result, companies don't have to wait for updates to see what's happening. Businesses can oversee inventory, keep tabs on sales, and analyze performance at any time using real-time data analysis.
Quick modifications can be done to prevent more serious issues if something is not going as intended. Additionally, this function facilitates quick and precise decision-making. Real-time data, for instance, can instantly indicate when a product is selling out so that additional stock can be ordered. It keeps everyone in the company informed and in sync.
Businesses may remain ahead of the competition, operate more effectively, and give their clients better service by utilizing real-time data.
Automation
Automation features in SAP ERP ECC help businesses streamline repetitive tasks, reducing manual effort and errors. The system handles monotonous tasks for you, such as data entry, invoice creation, and payroll processing.
This lowers the possibility of errors and saves a great deal of time. When a sale is made, for instance, an ERP system optimization might instantly update inventory data or send invoices to clients. It also guarantees the proper operation of crucial procedures, such as timely employee payments.
Employees can concentrate on more significant work rather than tedious duties thanks to ERP automation. Businesses operate more efficiently and without delays as a result. All things considered, automation simplifies tasks and maintains organization.
Data Analytics
ERP systems assist companies in understanding their performance through data analytics and visualization. They gather and examine data from several business areas, such as sales, inventory, and expenses. This aids businesses in identifying what is effective and what requires development.
Businesses can discover where they are overspending or which products are selling the best, for instance. The information is simple to interpret when presented in the form of charts and graphs. These insights assist businesses in planning for the future and making wise decisions.
Businesses may enhance operations, save costs, and expand more effectively by utilizing data analytics and visualization. It transforms complicated data into information that is clear and practical.
Business Process Controls
Business process controls are used by ERP systems to ensure that everything functions properly and complies with industry standards. These controls assist companies in establishing uniform procedures for managing inventory, collecting payments, and authorizing orders.
Businesses can increase productivity and prevent errors by implementing these measures. For instance, they can verify that an order is correct before shipping it out if the restrictions are in place. Errors are decreased and time is saved. Additionally, business process controls protect companies from legal problems by ensuring that they adhere to crucial regulations.
These technologies help businesses stay organized, streamline processes, and concentrate on expansion. It's similar to having a manual to assist you always do things correctly.
Reporting
ERP systems generate comprehensive reports that facilitate firms' comprehension of their performance. Important topics like sales trends, inventory levels, and financial performance are included in these reports. For instance, a company may monitor how well its items are selling or how much stock it has left.
This enables users to make wiser choices, such as placing larger orders or concentrating on well-liked items. ERP systems can give businesses a comprehensive picture of their financial situation by displaying their earnings, costs, and potential areas for development.
Businesses can use these tools to monitor their development and make future plans. By compiling all the data in one location, reporting in ERP systems saves time. It helps businesses develop and thrive by simplifying and making valuable complex data.
Integrations
ERP systems generate comprehensive reports that facilitate firms' comprehension of their performance, making it essential to evaluate different types of ERP software based on reporting needs, and different ERP system levels provide varying reporting functionalities. Important topics like sales trends, inventory levels, and financial performance are included in these reports. For instance, a company may monitor how well its items are selling or how much stock it has left.
This enables users to make wiser choices, such as placing larger orders or concentrating on well-liked items. ERP systems can give businesses a comprehensive picture of their financial situation by displaying their earnings, costs, and potential areas for development. While selecting a solution, businesses should explore kinds of ERP to understand the different functionalities available in modern ERP systems.
This increases productivity and facilitates work management. By providing all teams with the same information, integrations also improve teamwork. ERP systems guarantee that companies have a single platform on which all of their tools are integrated, resulting in more efficient and well-organized work. Integrating ERP systems with other tools can be complex, but ERP Consulting Services ensure seamless connectivity.
Single Database
All company data is kept in a single database by ERP systems. This implies that all data is stored in one location, including inventory levels, sales records, and customer information. Finding and using data fast is made simple with a single database. Because everyone utilizes the same current information, mistakes are also less likely to be made.
For instance, when a sale is made, the finance team may immediately view the transaction and the inventory is promptly updated. Since all departments share the same data, this configuration enhances teamwork. Additionally, it streamlines and expedites corporate procedures. Businesses can run their operations more effectively and make better judgments based on correct information when everything is centralized.
Manufacturing
By arranging duties like production planning and quality control, ERP systems streamline manufacturing procedures. These systems assist companies in determining what, how much, and when to produce.
By doing this, waste is decreased and timely product delivery is guaranteed. Manufacturers can monitor every stage, from raw materials to final products, with ERP. By keeping an eye on manufacturing and identifying issues early, it also guarantees high standards of quality.
Because they have access to the same information, teams can collaborate more effectively. For instance, the system automatically modifies production schedules in response to an order. Everything functions smoothly as a result. ERP systems are an effective way for manufacturers to cut expenses, save time, and provide their consumers with high-quality products.
CRM
To assist firms in managing client contacts, ERP systems frequently incorporate client Relationship Management (CRM) functionalities.
Businesses may monitor sales, communications, and client demands with the help of these technologies. CRM makes it easier for organizations to manage sales funnels, follow up on leads, and arrange contact information. It enables groups to collaborate in order to provide superior customer service and forge closer bonds with clients.
For instance, the system can notify a salesperson about the status of an order or remind them to call a customer. Businesses can more easily provide individualized services by using CRM in conjunction with ERP systems to better understand customer behavior and preferences. Better client loyalty and satisfaction result from this.
Sales Management
ERP systems track and organize sales orders to assist organizations with sales management. They let companies to handle payments, guarantee on-time delivery, and follow up with clients.
ERP makes it simple for businesses to monitor sales activity and client relationships. Sales staff can use the system to determine when to refill, how many things are in stock, and which products are popular. From accepting orders to delivering goods, it also aids in streamlining the complete sales process.
ERP sales management tools guarantee that clients receive their items on schedule and that the sales staff operates effectively. Businesses can increase sales performance and maintain customer satisfaction by streamlining the sales process.
Marketing
To assist companies in managing their marketing initiatives, several ERP systems provide marketing features. Tracking leads, customer contacts, and the effectiveness of marketing campaigns is made simple by these tools.
Businesses can use these tools to track consumer replies, send emails automatically, and assess the effectiveness of each campaign. It also aids companies in determining the most effective marketing techniques. Businesses may enhance their future efforts and make better judgments by evaluating marketing effectiveness.
By concentrating on tactics that attract the greatest number of clients, this helps save time and money. ERP systems with marketing capabilities help companies increase revenue and build relationships with clients.
HR Management
ERP systems combine the tasks of human capital management (HCM) into a single platform. This covers hiring, salary, and staff supervision.
These features make it simple for enterprises to workforce management solutions. They are capable of managing tasks including employing new personnel, monitoring employee performance, and making on-time employee payments. Businesses may more easily arrange and keep all of their employee data in one location using this solution.
Additionally, it assists companies in adhering to labor rules and regulations. Businesses may cut down on errors and save time by automating HR management System. Businesses can concentrate on growth and development and enhance personnel management with ERP solutions.
Supply Chain and Purchasing
ERP systems supervise logistics, inventory, and procurement, assisting companies in managing their supply chains. To make sure everything goes without a hitch, these systems monitor the movement of commodities from suppliers to consumers.
ERP makes it simple for companies to order goods, monitor inventory levels, and keep tabs on purchases. By doing this, stockouts and overstocking are prevented. Additionally, the technology offers real-time data, enabling companies to make well-informed supply chain decisions.
By automating processes like supplier management and order processing, it increases efficiency. Businesses may cut expenses and boost productivity by optimizing the supply chain. ERP systems simplify and improve the accuracy of process management from procurement to delivery.
What Are the Differences Between ERP Systems and FP&A Software?
.webp)
While both FP&A (Financial Planning and Analysis) software and ERP systems are instruments for managing business operations, their objectives are distinct. ERP systems aim to increase overall efficiency by integrating company activities such as manufacturing, inventory, and finance.
These technologies assist in tracking many business areas and automating processes. However, the primary functions of FP&A software are forecasting tools, budgeting, and financial planning. It assists companies in managing their budgets and forecasting their financial future.
FP&A software helps firms prepare for success by focusing on financial factors, whereas ERP systems offer a wide picture of corporate activity. Although these tools are useful, they fulfill different purposes in a company.
When to Use ERP Software
ERP software is ideal for companies looking to enhance and manage several aspects of their operations, such as finance, human resources (HR), and inventories. It assists businesses in streamlining procedures so that everything operates smoothly and effectively.
ERP software is a fantastic option if your company has numerous departments that must collaborate and exchange information. Businesses can select the ERP adoption strategy that best suits their needs from a variety of solutions, including On-premises ERP and cloud-based options.
ERP software combines inventory monitoring, payroll systems, and client order management into a one system. This makes it simpler to stay on top of things and steer clear of errors.
Whom to Use FP&A Software For
For companies that want assistance with forecasting, budgeting, and financial analysis, Financial Planning and Analysis (FP&A) software is ideal. It provides finance teams with strong capabilities to forecast financial results and make appropriate plans. There are various types of ERP packages available, ranging from cloud-based to on-premise solutions, each designed for different business needs.
Businesses can generate precise financial reports and examine trends with FP&A software to improve decision-making tools. It assists companies in assessing their financial situation and establishing reasonable objectives. FP&A software is an excellent option if you need to increase the accuracy of your planning, prepare for the future, or manage cash flow.
It assists financial teams in attentively examining data and making more informed decisions for the expansion of the company. Many industries benefit from ERP solutions, but who are the primary users of ERP systems? Typically, large corporations, small businesses, and even non-profits leverage ERP to streamline operations.
Conclusion
ERP systems are an excellent resource for companies of all sizes. They offer a centralized platform for managing many business operations, including inventories, finance, and human resources. Businesses may cut expenses and increase efficiency with the correct ERP system, and exploring what are the types of ERP ensures they choose the most suitable option, and knowing what ERP systems are available helps in making an informed decision.
Businesses can expand without fear of outgrowing the system thanks to ERP scalability. It can change as your company grows. You can guarantee a seamless implementation and maximize the functionality of your system by adhering to ERP Best Practices. Before implementation, businesses must research ERP systems names to identify leading providers and their unique offerings.
The correct ERP helps maximize business operations, regardless of whether you go with a customized system like Deltek or a cloud-based one like Oracle NetSuite. Businesses find it simpler to grow and flourish in the long run as a result. Check out another blog The Ultimate Guide to Enterprise Software Development
Frequently Asked Questions
.webp)
What is an ERP system?
Software that integrates numerous company processes is known as an ERP system, or enterprise resource planning system. It combines human resources, inventories, and finance into a single, user-friendly platform.
What does ERP stand for?
Enterprise Resource Planning is referred to as ERP. It alludes to a platform that enables companies handle a variety of functions, including inventories, finance, and human resources.
Is SAP an ERP system?
It's true that SAP S/4HANA is an ERP. Large corporations frequently utilize it to effectively handle commercial operations including finance, supply chain, and human resources.
Is QuickBooks an ERP system?
The primary function of QuickBooks is accounting software. It is mostly intended for small enterprises to handle banking, invoicing, and routine business processes, even if it has certain ERP features.
Is Oracle an ERP system?
Oracle does offer ERP systems, including Oracle NetSuite. With a consolidated platform, these solutions assist companies of all sizes in effectively managing HR, supply chains, and finances.
.webp)
